OpenFOAM
OpenFOAM is a C++ library for solving PDEs with the special focus on Computional Fluid Dynamics with a large user base in academia and industry. With it incompressible, compressible, reacting and multiphase flow with numerous models can be simulated. These different flow types are all addressed by multiple applications that all have unique set of input parameters. The case consists of 3 main folder the “system”, “constant” and the “time directories” as described in the OpenFOAM user guide. The “system” folder mainly contains the numerical parameters of a simulation, the “constant” folder the physical model such as the fluid properties or the selected turbulence model and the “time folder” store the computed fields.
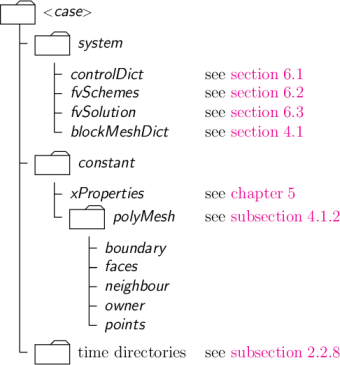
The case structure contains multiple files providing the input for the solvers.
Extending
One of the biggest strength of OpenFOAM is its extendibility achieved by its runtime selection mechanism. This plugin architecture enables us to specify the class used by the solver by changing a keyword in a file. This abstract concept can easily be demonstrated on the tutorials case: tutorials/multiphase/interIsoFoam/weirOverflow by changing the file constant/turbulenceProperties to:
/*--------------------------------*- C++ -*----------------------------------*\
| ========= | |
| \\ / F ield | OpenFOAM: The Open Source CFD Toolbox |
| \\ / O peration | Version: v2106 |
| \\ / A nd | Website: www.openfoam.com |
| \\/ M anipulation | |
\*---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
FoamFile
{
version 2.0;
format ascii;
class dictionary;
location "constant";
object turbulenceProperties;
}
// * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * //
simulationType RAS; // options: LES RAS laminar)
RAS
{
RASModel falseInput; // also known as banana trick
turbulence on;
printCoeffs on;
}
// ************************************************************************* //
If we run the testcase by ./Allrun in tutorials/multiphase/interIsoFoam/weirOverflow the solver crashes with following error message:
--> FOAM FATAL IO ERROR: (openfoam-2106)
Unknown RAS model type falseInput
Valid RAS model types :
18
(
LRR
LamBremhorstKE
LaunderSharmaKE
LienCubicKE
LienLeschziner
RNGkEpsilon
SSG
ShihQuadraticKE
SpalartAllmaras
kEpsilon
kEpsilonPhitF
kOmega
kOmegaSST
kOmegaSSTLM
kOmegaSSTSAS
kkLOmega
qZeta
realizableKE
)
and we get the list of available classes (here :RAS-turbulence models). All turbulence models are childs of an abstract class that implement the runtimeselection mechanism. This design is used in every physical model, boundary condition and numerical model. However ,this feature alone only simplyfies the usage of OpenFOAM but doesnot increase its extendibility. This is addressed by loading addtional libraries at runtime that offer new classes with new physical model, boundary condition and numerical model. The additional libraries need to be specified in the controlDict with the lib keyword:
libs(newTurbModels newBCs)
The libraries libnewTurbModels.so and newBCs.so would provide new boundary conditions and turbulence models. Additional libraries can also be loaded in the functionObjects that allow us to post process our results or manipulate OpenFOAM to use as done in the precice library
functions
{
probes
{
type probes;
libs (sampling);
...
}
}