Generate FMU from an OpenFOAM case
pip install fmu4foam
creating an FMU from OpenFOAM is simple and similar to the libary PythonFMU which is achieved with just one line:
fmu4foam build -f TempControl.py -of OfCase/ --no-external-tool
OpenFOAM modifications
As in the previous method, we extend OpenFOAM with the additional libraries and add the following lines to the system/controlDict:
// loads addtional input and output function/class
// e.g. new boundary conditions.
libs(externalComm);
// includes the file system/simulationParameters in the controlDict
// and enables the definition of Variables marked with a $
// only look in the current directory and is short for:
// #include "<case>/system/simulationParameters"
#include "simulationParameters"
functions
{
FMUController
{
type FMUController; // execute functionObjects FMUController
libs (FMUController); // load "libFMUController.so"
host $host; // connect to ip specified in simulationParameters
port $port; // connect to port specified in simulationParameters
}
}
the controlDict specifies two variables: host and port that need to be specified in the system/simulationParameters:
/*--------------------------------*- C++ -*----------------------------------*\
| ========= | |
| \\ / F ield | OpenFOAM: The Open Source CFD Toolbox |
| \\ / O peration | Version: v2012 |
| \\ / A nd | Website: www.openfoam.com |
| \\/ M anipulation | |
\*---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
FoamFile
{
version 2.0;
format ascii;
class dictionary;
location "system";
object simulationParameters;
}
// * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * //
host "127.0.0.1"; // defines host
port 8000; // defines port
STDGRAD Gauss linear;
STDLAP Gauss linear uncorrected;
writeInterval 0.1;
// ************************************************************************* //
The host and port variable are specified in the FMU generation base class.
- host -> connect to other computer
- port -> port on that computer
- outputPath -> extract dir of the OpenFOAM Case
- oscmd -> name of the system command (enables exectuion on docker or wsl for windows users in the future)
- arguments -> additional parameters for the Allrun script e.g. source environment in script
NOTE: The host variable needs to be quoted. To achieve this, we define it with two qoutes ‘“Name of the Variable”’. The other variables require no specific highlighting.
class OF2Fmu(Fmi2Slave):
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
super().__init__(**kwargs)
#local host aka this computer
self.host = '"127.0.0.1"' # Note the double quotes
self.port = 8000 # port see above
self.outputPath = "OFCase" # extract path relative to FMU
self.oscmd = "bash -i" # system command to execute the Allrun
# additional parameters for the Allrun script
# of2012 to source the enviroment in the Allrun script
self.arguments = ""
self.register_variable(String("host",
causality=Fmi2Causality.parameter, variability=Fmi2Variability.tunable))
self.register_variable(Integer("port",
causality=Fmi2Causality.parameter, variability=Fmi2Variability.tunable))
self.register_variable(String("outputPath",
causality=Fmi2Causality.parameter, variability=Fmi2Variability.tunable))
self.register_variable(String("oscmd",
causality=Fmi2Causality.parameter, variability=Fmi2Variability.tunable))
self.register_variable(String("arguments",
causality=Fmi2Causality.parameter, variability=Fmi2Variability.tunable))
FMU generation input file
The last part in the generation of the FMU is a python file specified after -f TempControl.py:
from pythonfmu.variables import Boolean
from FMU4FOAM import Fmi2Causality, Fmi2Variability, Real, Boolean , Integer, String
from FMU4FOAM import OF2Fmu
class TempControl(OF2Fmu):
author = "John Doe"
description = "A simple description"
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
super().__init__(**kwargs)
# Input Output variable
self.Qin = 0.0
self.dTout = 0.0
self.Tout = 298.0
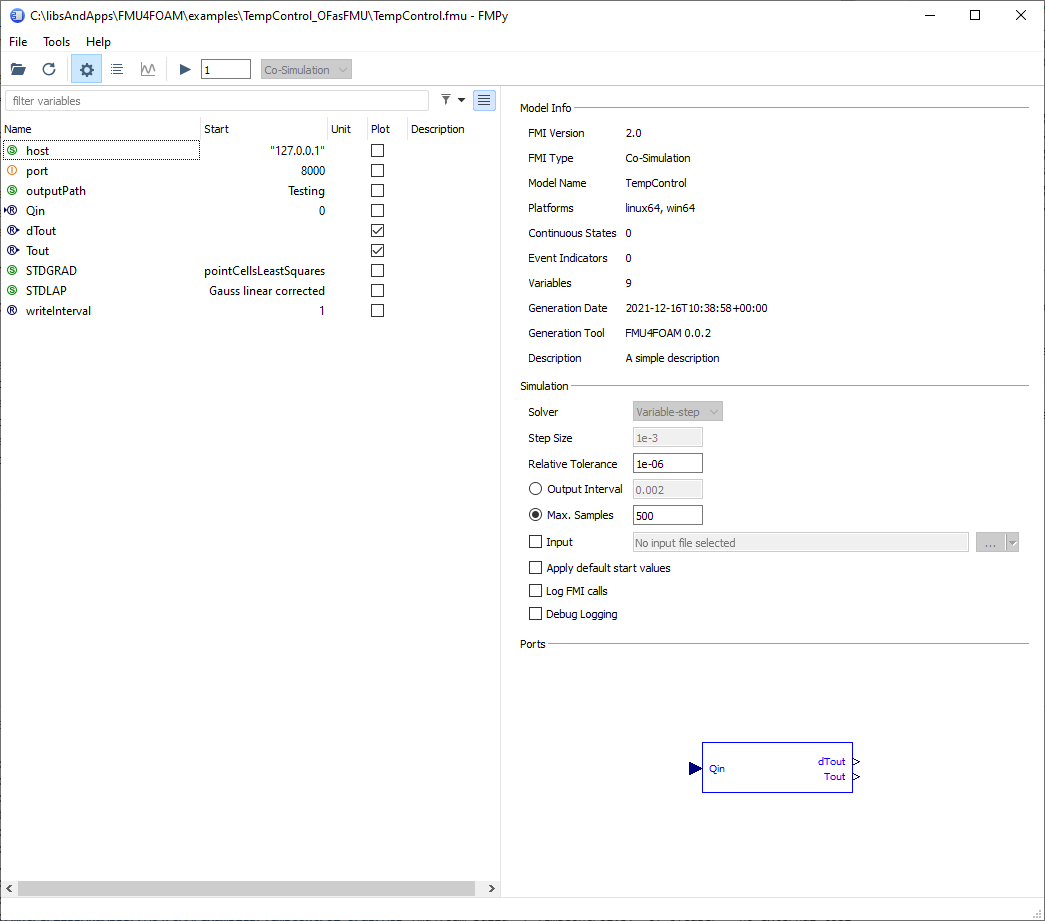
self.host = '"192.168.1.200"' # overwrite the ip
self.outputPath = "Testing" # will extract the OfCase files in Testing
self.register_variable(Real("Qin", causality=Fmi2Causality.input))
self.register_variable(Real("dTout", causality=Fmi2Causality.output))
self.register_variable(Real("Tout", causality=Fmi2Causality.output))
# Parameters
self.writeInterval = 1.0 # changes outputInterval of the solver
self.STDLAP = "Gauss linear corrected" # possiblity to change discreization
self.STDGRAD = "pointCellsLeastSquares" # possiblity to change discreization
self.register_variable(String("STDGRAD",
causality=Fmi2Causality.parameter, variability=Fmi2Variability.tunable))
self.register_variable(String("STDLAP",
causality=Fmi2Causality.parameter, variability=Fmi2Variability.tunable))
self.register_variable(Real("writeInterval",
causality=Fmi2Causality.parameter, variability=Fmi2Variability.tunable))
The FMU standard defines three relevant causalities:
- input -> input parameters that change in time (assume to be REAL aka floats)
- output -> output parameters that change in time (assume to be REAL aka floats)
- parameter -> set at the start of the simulation and does not change (strings, float, interges, boolean)
NOTE: FMI standard 2.0 only allows for scalar data transfer but does not support data fields so an OpenFOAM vector would be 3 input variables (This will change in FMI 3.0)
In the example above we specify following causalities:
- input:
- Qin
- input:
- Tout
- dTout
- parameter
- writeInterval
- STDLAP
- STDGRAD
- host (from base class)
- port (from base class)
- outputPath (from base class)
- oscmd (from base class)
- arguments (from base class)
These parameters can be modified before running the FMU for example with the fmpy by calling
python -m fmpy.gui TempControl.fmu